Periodontal disease (gum disease)
Gingivitis
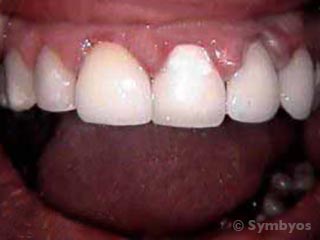
Figure 1: A moderately severe case of gingivitis characterized by swollen gums (gingiva), red tissue margins, and bleeding on light stimulation. The condition is usually due to poor oral hygiene.
Gingivitis is a reversible inflammation of the gums (gingiva), with no breakdown of the attachment fibers connecting them to the teeth and underlying bone. Gingivitis is the earliest and simplest form of gum disease. It is characterized by red, puffy gums that bleed easily (Figure 1), but may or may not be sore. The disease is most often caused by bacterial plaque, and is generally reversible with removal of the plaque and excellent oral hygiene.
If ignored, the bacteria and inflammation causing gingivitis will destroy the periodontal attachment fibers between the gums and teeth, allowing bacteria to invade and destroy the underlying bone. When the attachment fibers have been lost, the diagnose becomes one of periodontal disease (gum disease/periodontitis).
Periodontal disease
Untreated gingivitis can progress to the point where the gingival attachment fibers to tooth and bone are lost; and beyond that to the point where bone destruction results (Figure 2). This bacterial illness is called periodontal disease (or periodontitis), and is the number one cause of tooth loss in adults. It is also referred to as gum disease and by the antiquated term, pyorrhea.
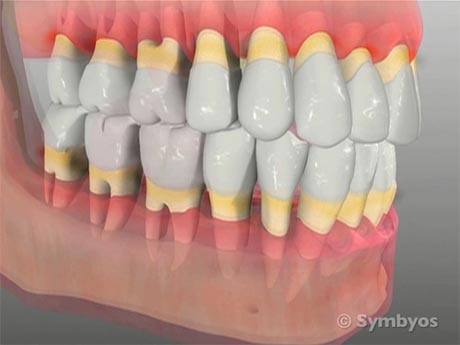
Figure 2: Advanced periodontal disease. If more than 40% of the tooth-supporting (alveolar) bone has been destroyed by periodontal disease, the disease is considered severe, or advanced. Allowing the disease to progress to this point introduces significant general health risks.
Periodontitis is not curable, but it can be controlled indefinitely through treatment by a dental professional, excellent home care, and regular follow-up with a general dentist or periodontist. It is important to note that there is evidence that periodontal disease and certain systemic illnesses are related, and that treating periodontal disease in the dentist’s chair before it progresses may prevent expensive medical treatment and life-threatening illness.